#which financial market is the stock market a part of
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Note
So like. Does Ellis even... have a job??? Or is he just kinda coasting through life?

#danganronpa: one shot#dros#fanganronpa#danganronpa#dros character asks#character q&a#ellis ortiz#I wasn’t sure if you wanted this to be a character as or not so you get one anyways#were it not a character ask I would say: Ellis’ lucky student talent is specifically related to being lucky financially/with gaining money#so that luck results in them finding themself with enough money on hand to not need to work#the stock market part is also essentially gambling just fancier a la monkeys in the stock market story#(the gist of which is that someone got 100 monkeys to participate in the stock market and 98 of their portfolios did better than#stock experts; more or less proving that doing well in stocks can be pretty random) -A
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Courses On Stock Trading
Introduction to Stock Trading
The Introduction to Stock Trading course provides beginners with a comprehensive overview of the stock market and trading practices. Participants learn the fundamental concepts and terminology related to stocks and trading. The course covers topics such as how the stock market functions, the role of stock exchanges, and the different types of stocks available. Participants also gain insights into trading platforms and brokerage accounts, enabling them to navigate the trading process effectively.

Technical Analysis
The Technical Analysis course is designed to equip participants with the skills needed to analyze stock price charts and identify potential trading opportunities. Participants learn about various technical indicators, chart patterns, and trend analysis techniques. They understand how to interpret support and resistance levels, moving averages, oscillators, and other technical tools. By the end of the course, participants will be able to make informed trading decisions based on technical analysis.
Fundamental Analysis
The Fundamental Analysis course focuses on evaluating the financial health and performance of companies to make trading decisions. Participants learn how to analyze financial statements, including balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements. They also understand how to assess key financial ratios, industry trends, and competitive positioning. Additionally, the course explores the impact of macroeconomic factors and news events on stock prices, enabling participants to make more accurate predictions.
Options Trading
The "Options Trading" course introduces participants to the world of options and teaches them how to incorporate these instruments into their trading strategies. Participants learn about the various types of options, including calls and puts, and gain an understanding of options pricing models. The course covers options trading strategies, including basic options trades, spreads, and hedging techniques. Participants also learn about managing risk associated with options trading and maximizing profit potential.
Risk Management and Psychology
The Risk Management and Psychology course emphasizes the importance of managing risk and maintaining a disciplined mindset while trading. Participants learn about different risk management techniques, including position sizing, stop-loss orders, and diversification. The course also focuses on the psychological aspects of trading, such as understanding and controlling emotions, developing discipline, and maintaining a trading journal. By the end of the course, participants will have a solid understanding of how to manage risk effectively and cultivate the right mindset for successful trading.
Overall, these courses provide a comprehensive foundation in stock trading, covering essential topics such as market analysis, technical and fundamental analysis, options trading, risk management, and trading psychology. Participants will gain the knowledge and skills necessary to make informed trading decisions and manage risks effectively in the dynamic world of stock markets.
#the price of company stocks already trading on the stock market are determined by supply and demand.#amzn stock#options trading on etoro#goog stock#msft stock#buy tesla stock on etoro#apple stock after hours#the financial market first started over 500 years ago with merchants trading debts.#sofi stock#frc stock#aapl stock#yahoo finance#pacw stock#which financial market is the stock market a part of?#most stock exchanges today use floor trading with human brokers.#premarket stock trading#amd stock#premarket trading#ford stock#apple stock price
0 notes
Text
if there’s a general problem I have with Dan Olson’s videos about financial scams (whose content I very much enjoy) is his emphasis on “laziness” as part of the appeal of these scams, that the concept of having passive income is laughable, not because private forms of passive income (such as rent, stocks, etc) are based on exploitation but because it means the people buying into it are lazy, and so a reason to mock the people duped by/engaging in these scams is because they are unwilling to work hard for their money like everyone else. like what’s very clearly appealing about these scams is that they promise an exit from wage-labour through petty forms of domination, such as subcontracting someone for below-minimum wages to write a manuscript for you that you then earn a profit from by self-publishing it on amazon. which is not a scam opportunity to be a lazy, immoral citizen, it’s a scam opportunity to become part of the exploiter class. “guy who is lazy” is not a coherent position in the market and thinking this way leads to goofy moralism about the value of a hard day’s work
523 notes
·
View notes
Text
Review: “My Investing Journey and Learning” by Carmen Mundt
Qualifications: I’m a journalist reporting on business, economics, and defense who’s been in the industry for 7 years — the last 3 have been at, debatably, the #1 business publication in the world.
Rating: 2/5 stars
Thoughts: I cannot believe I spent 39 euros on this.
This 39 page ebook provides incredibly basic information that can all be found in this article.
First: while the ebook is about 40 pages, it probably has about 10 pages of actual information in it, interspersed with inspirational quotes from Sheryl Sandberg and Warren Buffet, with some pictures of Carmen in Monaco.
There’s about 1 page of “introduction” from Carmen that talks about her upbringing and journey to university in London. I won’t comment too much on her personal story, but an important thing to note is that she says she came from a “traditional Spanish household” where her father was the breadwinner and her mother had no access to family finances. After the 2008 crash, her family couldn’t afford to send her to college. She moved to London, applied for a student loan, and began studying finance at a university while working part time.
Carmen very, very briefly mentioned her regrets as to her mother’s inability to access higher education, work, and family financial planning; she says she’d never want to be in that position. While literally only one sentence, I think it makes it clear who the audience for this ebook is: someone who has absolutely, positively, no idea about money.
(She also very, very briefly mentions “big changes in her personal life” that made a full-time job in finance “not sustainable,” leading to her move to Monaco. This is her only reference to George.)
The rest of the book very simply explains how to make a budget, set financial goals, invest in the stock market, and mitigate risk. The information was kinda factually correct, and was written in a coherent manner. I think that’s the highest praise I can give it.
Here’s the thing: like other reviewers have called out, I am pretty certain that Carmen didn’t write anything besides the introduction. Whole sections (and indeed the entire format of the ebook) were clearly ripped from the Female Invest introductory courses. (I spent 3 hours clicking through each course so I could find direct wording comparisons to make this claim. I really wouldn’t recommend it.) I do think she edited these sections, and she interjected a few personal sentences; but I believe that’s where her involvement ended.
From an expert perspective, a lot of the information is so simplistic as to be almost incorrect. This isn’t a “first day of Econ 101” ebook — this is a “freshman year of high school home ec class” ebook. (Did anyone else’s home ec classes teach budgeting, or just me?)
Here’s an example. In a section on stocks, Carmen/Female Invest writes: “Investing in stocks allows you to support companies and causes you care about while still making a profit.”
On a basic level, this is correct. Purchasing a stock technically means you’re buying a little bit of a company, and I guess therefore supporting it. But unless a company is IPOing, you’re buying those stocks from another investor — which means your purchase has no effect on the company. So it’s a little disingenuous to claim you’re somehow helping the company. The ebook is rife with this kind of thing.
Carmen pushed in her advertising posts that the Female Invest courses were a key supplement to her book. So obviously, I had to do those too. And holy shit, they were so much worse than the ebook. Some parts were blatantly incorrect on basic information (they claim markets are open 24/7, when most are only open 9am-4:30pm on weekdays) and have some of the most patronizing metaphors I have ever read. (One of the most egregious was comparing your investment portfolio to a pizza because “stocks, bonds, and ETFs” make up different “sizes of slices to make a whole pie”. This isn’t even an accurate equivalent — maybe a calzone, pasta, and pizza make up a whole meal? I don’t even know.)
I would not recommend buying this ebook unless you, too, were barred from even thinking about a stock by your traditional father. Even then, consider free sources.
A Disclaimer on disclosures: So, after @ohblimeygeorge sent me a reddit post also reviewing Carmen’s book that mentioned ad disclosures, I decided to dive into the regulations. In the U.S., influential advertising is regulated by the FTC — in the EU, it’s regulated by the EU Commission, which I believe Carmen would qualify under since she is a Spanish citizen who lives in Monaco. First, I looked at this legal brief on content monetization business models, and concluded that that the ebook likely falls under “affiliate marketing” as Carmen likely receives a percentage of each ebook sold through her link.
(An additional disclaimer: obviously, I don’t know the details of the deal Carmen has with Female Invest, but I’d think it unlikely that she isn’t getting paid for their collaboration. She mentioned in an Instagram story under her Female Invest highlight that she “tried purchasing equity but they were already too big for what I could afford” but “did buy a bit of their crowdfunding.” Since she doesn’t have equity, i.e. doesn’t own a piece of the company, it’d be weird if she was doing this for free.)
Back on topic. I next looked at this legal brief on advertising disclosures. It states that affiliate marketing must be disclosed: “you need to make sure your audiences understand that it’s advertising.” Disclosures can include hashtags and “mentioning” advertising in the caption. Carmen has not disclosed advertising in any of her Female Invest posts, and appears to be violating this regulation. (Interestingly, her only posts that follow disclosure requirements are her Tommy posts.)
It’s apparently not uncommon. An EU Commission study showed 80% of influencers in the EU do not properly disclose ads.
So, there’s that too.
#I spent waaaaaay too long doing female invest courses for this#I was just horrified and couldn’t stop!!#my verdict#unfortunately#is that this IS the equivalent of a weight loss ebook peddled by an ig baddie#disappointing but I suppose unsurprising#happy to answer more questions if u message me!#george russell#carmen montero mundt#carmen mundt
162 notes
·
View notes
Text
Astrology observation
All about your north node and your future spouse
Part 2
we will be starting by speaking about North node in the 8th house since it's a Scorpio ruled house deep meaningful love is seen here however the longevity of married life it's going to depend on your and future spouse healthy habits attitude towards life, for example you and your future spouse should do healthy diet or start eating vegetarian food also doing physical activity together will make the bond between you two stronger your future spouse is going to be loaded, financially speaking you will have a decent life with them you may even get inheritance after they die since the north note is two houses after your 7th house so it represents the second house of your future spouse chart your future spouse is one of the people who worked very hard to get what they want in life they're beginning wasn't really great so maybe this is a sign that when you meet your future spouse he will have the story about transformation from poverty to richness, your in-laws will play significant role in your married life this can cause some troubles because everybody's going to be in your business. Before getting into a relationship with any person you should pay attention to what they are hiding the eighth house is all about secrets and I know people who had their north node in their eighth House and after getting a relationship with someone they figured out that at the same time they had another girlfriend or a child they're hiding Etc so you need to pay attention to ask questions before you get married. Also your future spouse could have relationship to politics or military or work in it. You could meet your future spouse while doing research on a specific subject(cult, stock market, lawns).

No let's talk about North node in your 10th house it is fourth houses from your 7th house which typically represent the fourth house in your future spouse chart and the fourth house is all about family the mother Homeland Etc so if future spouse is going to be family oriented person in some cases your mom will have a great relationship with either your future spouse or she will know the family if your future spouse already, your future spouse coul be working in their family business or maybe they took over their family, here's the twist the mother of your future spouse will have significant role in your marriage if their mother is present in their life you better know that they are their mommy child however if the mother is not present they will count on you acting like their mother they will search mother Love In you another thing this person could have a mom that is working hard since the day they were born and these kind of people will expect you to kind of be like their mom they want someone who wants to work and work hard if this is a woman you are looking for then this woman is counting on you working hard and if you are looking for men this man will want you to work hard ,they will want you to be independent, this person could live near you you may be me this person while you working , also the 10th house is relay is ruled naturally by Saturn so an older partner is seen of course if Saturn is not placed positively in your chart your future spouse could be younger than you however the way they think and the way they act is much older than their age.

Now if your north node is in the 12th house you could have this type of love story when you hate your future spouse at first and then you fall in love with them your future spouse could have bullied you first, the 12th house is sixth house away from the 7th house so it represent the sixth house in your future spouse chart and it's not normally ruled by the sign of Leo therefore ruled by the Sun, The 6th house represent enemies, warriors, diseases and Etc when I'm getting is that your future spouse could have been through a huge transformation in their life for example you know these people who like overweight and they work hard at the gym to become healthy or these people who felt a lot with certain disease and then they got out of it Victorious, your partner will get your back and frankly your future spouse could be your soulmate they are intuitive and emotional, however the 12th house is the house of Hidden enemies so at some point your future spouse can get really annoyed with you and they may keep their anger to themselves to the point where they will explode on you so maybe try to talk about problems and not bottle them up, because obviously you don't want to be in marriage that can mess with your mental health. Your future spouse could be wearing in the health sector , therapist, artist , Physic or a policeman a fireman I mean they supposedly working to keep people safe.
Part 1
Do not Copy or rewrite my shit without asking for my permission.
292 notes
·
View notes
Text
On the evening of November 19, art adviser Adam Biesk was finishing work at his California home when he overheard a conversation between his wife and son, who had just come downstairs. The son, a kid in his early teens, was saying he had made a ton of money on a cryptocurrency that he himself had created.
Initially, Biesk ignored it. He knew that his son played around with crypto, but to have turned a small fortune before bedtime was too far-fetched. “We didn’t really believe it,” says Biesk. But when the phone started to ring off the hook and his wife was flooded with angry messages on Instagram, Biesk realized that his son was telling the truth—if not quite the full story.
Earlier that evening, at 7:48 pm PT, Biesk’s son had released into the wild 1 billion units of a new crypto coin, which he named Gen Z Quant. Simultaneously, he spent about $350 to purchase 51 million tokens, about 5 percent of the total supply, for himself.
Then he started to livestream himself on Pump.Fun, the website he had used to launch the coin. As people tuned in to see what he was doing, they started to buy into Gen Z Quant, leading the price to pitch sharply upwards.
By 7:56 pm PT, a whirlwind eight minutes later, Biesk's son’s tokens were worth almost $30,000—and he cashed out. “No way. Holy fuck! Holy fuck!” he said, flipping two middle fingers to the webcam, with tongue sticking out of his mouth. “Holy fuck! Thanks for the twenty bandos.” After he dumped the tokens, the price of the coin plummeted, so large was his single trade.
To the normie ear, all this might sound impossible. But in the realm of memecoins, a type of cryptocurrency with no purpose or utility beyond financial speculation, it’s relatively routine. Although many people lose money, a few have been known to make a lot—and fast.
In this case, Biesk’s son had seemingly performed what is known as a soft rug pull, whereby somebody creates a new crypto token, promotes it online, then sells off their entire holdings either swiftly or over time, sinking its price. These maneuvers occupy something of a legal gray area, lawyers say, but are roundly condemned in the cryptosphere as ethically dubious at the least.
After dumping Gen Z Quant, Biesk’s son did the same thing with two more coins—one called im sorry and another called my dog lucy—bringing his takings for the evening to more than $50,000.
The backlash was swift and ferocious. A torrent of abuse began to pour into the chat log on Pump.Fun, from traders who felt they had been swindled. “You little fucking scammer,” wrote one commenter. Soon, the names and pictures of Biesk, his son, and other family members were circulating on X. They had been doxed. “Our phone started blowing up. Just phone call after phone call,” says Biesk. “It was a very frightening situation.”
As part of their revenge campaign, crypto traders continued to buy into Gen Z Quant, driving the coin’s price far higher than the level at which Biesk’s son had cashed out. At its peak, around 3:00 am PT the following morning, the coin had a theoretical total value of $72 million; the tokens the teenager had initially held were worth more than $3 million. Even now the trading frenzy has died down, they continue to be valued at twice the amount he received.
“In the end, a lot of people made money on his coin. But for us, caught in the middle, there was a lot of emotion,” says Biesk. “The online backlash became so frighteningly scary that the realization that he made money was kind of tempered down with the fact that people became angry and started bullying.”
Biesk concedes to a limited understanding of crypto. But he sees little distinction between what his son did and, say, playing the stock market or winning at a casino. Though under California law someone must be at least 18 years old to gamble or invest in stocks, the unregulated memecoin market, which has been compared to a “casino” in risk profile, had given Biesk’s teenage son early access to a similar arena, in which some must lose for others to profit. “The way I understand it is he made money and he cashed out, which to me seems like that's what anybody would've done,” says Biesk. “You get people who are cheering at the craps table, or angry at the craps table.”
Memecoins have been around since 2013, when Dogecoin was released. In the following years, a few developers tried to replicate the success of Dogecoin, making play of popular internet memes or tapping into the zeitgeist in some other way in a bid to encourage people to invest. But the cost and complexity of development generally limited the number of memecoins that came to market.
That equation was flipped in January with the launch of Pump.Fun, which lets people release new memecoins instantly, at no cost. The idea was to give people a safer way to trade memecoins by standardizing the underlying code, which prevents developers from building in malicious mechanisms to steal funds, in what’s known as a hard rug pull.
“Buying into memecoins was a very unsafe thing to do. Programmers could create systems that would obfuscate what you are buying into and, basically, behave as malicious actors. Everything was designed to suck money out of people,” one of the three anonymous cofounders of Pump.Fun, who goes by Sapijiju, told WIRED earlier in the year. “The idea with Pump was to build something where everyone was on the same playing field.”
Since Pump.Fun launched, millions of unique memecoins have entered the market through the platform. By some metrics, Pump.Fun is the fastest-growing crypto application ever, taking in more than $250 million in revenue—as a 1 percent cut of trades on the platform—in less than a year in operation.
However, Pump.Fun has found it impossible to insulate users from soft rug pulls. Though the platform gives users access to information to help assess risk—like the proportion of a coin belonging to the largest few holders—soft rug pulls are difficult to prevent by technical means, claims Sapijiju.
“People say there’s a bunch of different stuff you can do to block [soft rug pulls]—maybe a sell tax or lock up the people who create the coin. Truthfully, all of this is very easy to manipulate,” he says. “Whatever we do to stop people doing this, there’s always a way to circumnavigate if you’re smart enough. The important thing is creating an interface that is as simple as possible and giving the tools for users to see if a coin is legitimate or not.”
The “overwhelming majority” of new crypto tokens entering the market are scams of one form or another, designed expressly to squeeze money from buyers, not to hold a sustained value in the long term, according to crypto security company Blockaid. In the period since memecoin launchpads like Pump.Fun began to gain traction, the volume of soft rug pulls has increased in lockstep, says Ido Ben-Natan, Blockaid founder.
“I generally agree that it is kind of impossible to prevent holistically. It’s a game of cat and mouse,” says Ben-Natan. “It’s definitely impossible to cover a hundred percent of these things. But it definitely is possible to detect repeat offenders, looking at metadata and different kinds of patterns.”
Now memecoin trading has been popularized, there can be no putting the genie back in the bottle, says Ben-Natan. But traders are perhaps uniquely vulnerable at present, he says, in a period when many are newly infatuated with memecoins, yet before the fledgling platforms have figured out the best way to protect them. “The space is immature,” says Ben-Natan.
Whether it is legal to perform a rug pull is also something of a gray area. It depends on both jurisdiction and whether explicit promises are made to prospective investors, experts say. The absence of bespoke crypto regulations in countries like the US, meanwhile, inadvertently creates cloud cover for acts that are perhaps not overtly illegal.
“These actions exploit the gaps in existing regulatory frameworks, where unethical behavior—like developers hyping a project and later abandoning it—might not explicitly violate laws if no fraudulent misrepresentation, contractual breach, or other violations occur,” says Ronghui Gu, cofounder of crypto security firm CertiK and associate professor of computer science at Columbia University.
The Gen Z Quant broadcast is no longer available to view in full, but in the clips reviewed by WIRED, at no point does Biesk’s son promise to hold his tokens for any specific period. Neither do the Pump.Fun terms of use require people to refrain from selling tokens they create. (Sapijiju, the Pump.Fun cofounder, declined to comment on the Gen Z Quant incident. They say that Pump.Fun will be “introducing age restrictions in future,” but declined to elaborate.)
But even then, under the laws of numerous US states, among them California, “the developer likely still owes heightened legal duties to the investors, so may be liable for breaching obligations that result in loss of value,” says Geoffrey Berg, partner at law firm Berg Plummer & Johnson. “The developer is in a position of trust and must place the interests of his investors over his own.”
To clarify whether these legal duties apply to people who release memecoins through websites like Pump.Fun—who buy into their coins like everyone else, albeit at the moment of launch and therefore at a discount and in potentially market-swinging quantities—new laws may be required.
In July 2026, a new regime will take effect in California, where Biesk’s family lives, requiring residents to obtain a license to take part in “digital financial asset business activity,” including exchanging, transferring, storing or administering certain crypto assets. President-elect Donald Trump has also promised new crypto regulations. But for now, there are no crypto-specific laws in place.
“We are in a legal vacuum where there are no clear laws,” says Andrew Gordon, partner at law firm Gordon Law. “Once we know what is ‘in bounds,’ we will also know what is ‘out of bounds.’ This will hopefully create a climate where rug pulls don't happen, or when they do they are seen as a criminal violation.”
On November 19, as the evening wore on, angry messages continued to tumble in, says Biesk. Though some celebrated his son's antics, calling for him to return and create another coin, others were threatening or aggressive. “Your son stole my fucking money,” wrote one person over Instagram.
Biesk and his wife were still trying to understand quite how their son was able to make so much money, so fast. “I was trying to get an understanding of exactly how this meme crypto trading works,” says Biesk.
Some memecoin traders, sensing there could be money in riffing off the turn of events, created new coins on Pump.Fun inspired by Biesk and his wife: QUANT DAD and QUANTS MOM. (Both are now practically worthless.)
Equally disturbed and bewildered, Biesk and his wife formed a provisional plan: to make all public social media accounts private, stop answering the phone, and, generally, hunker down until things blew over. (Biesk’s account is active at the time of writing.) Biesk declined to comment on whether the family made contact with law enforcement or what would happen to the funds, saying only that his son would “put the money away.”
A few hours later, an X account under the name of Biesk’s son posted on X, pleading for people to stop contacting his parents. “Im sorry about Quant, I didnt realize I get so much money. Please dont write to my parents, I wiill pay you back [sic],” read the post. Biesk claims the account is not operated by his son.
Though alarmed by the backlash, Biesk is impressed by the entrepreneurial spirit and technical capability his son displayed. “It’s actually sort of a sophisticated trading platform,” he says. “He obviously learned it on his own.”
That his teenager was capable of making $50,000 in an evening, Biesk theorizes, speaks to the fundamentally different relationship kids of that age have with money and investing, characterized by an urgency and hyperactivity that rubs up against traditional wisdom.
“To me, crypto can be hard to grasp, because there is nothing there behind it—it’s not anything tangible. But I think kids relate to this intangible digital world more than adults do,” says Biesk. “This has an immediacy to him. It’s almost like he understands this better.”
On December 1, after a two-week hiatus, Biesk’s son returned to Pump.Fun to launch five new memecoins, apparently undeterred by the abuse. Disregarding the warnings built into the very names of some of the new coins—one was named test and another dontbuy—people bought in. Biesk’s son made another $5,000.
43 notes
·
View notes
Text


Propaganda
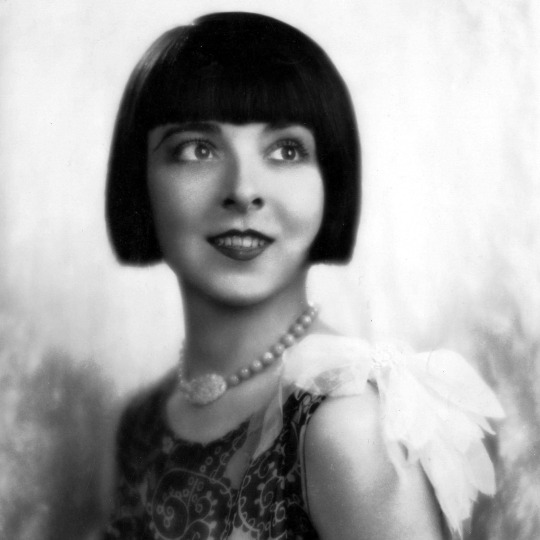
Colleen Moore (Flaming Youth, Ella Cinders)— One of the highest paid, most in-demand actresses of the silent film era, Colleen Moore defied genre and kept herself one step ahead of the competition (and although Moore was the OG flapper, her longtime rival Clara Bow would become more famous for the image) as well as invested her earnings to ensure her financial security after she retired. She even wrote a book all about investing in the stock market! Moore also nurtured a passion for dollhouses throughout her life and helped design and curate The Colleen Moore Dollhouse, which has been a featured exhibit at the Museum of Science and Industry in Chicago since the early 1950s.
Lilian Harvey (Die Drei von der Tankstelle, Der Kongreß Tanzt, Glückskinder)— Lilian Harvey was one of the most popular German film stars of her time, appearing alongside frequent co-star Willy Fritsch like a European version of Ginger Rogers and Fred Astaire. She had it all: she could act, she could dance, she could sing, she was hot, and she wasn't afraid to stick it to the Nazis. During the 1930s, she remained in contact with her Jewish friends and colleagues, which earned her the scrutiny of the Gestapo. When choreographer Jens Keith was arrested for having a sexual relationship with another man, Lilian posted his bail, allowing him to escape to France. She was eventually forced to flee Germany herself, and her film career never recovered. She is perhaps best known to American filmgoers from her brief mention in "Inglourious Basterds," when Joseph Goebbels insists that her name not be mentioned in his presence.
This is round 1 of the tournament. All other polls in this bracket can be found here. Please reblog with further support of your beloved hot sexy vintage woman.
[additional propaganda submitted under the cut]
Lilian Harvey:

Colleen Moore:
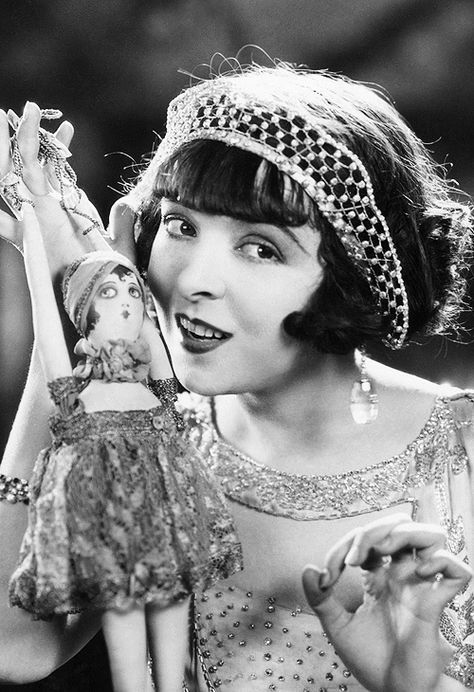


Colleen is charming and funny, she was one of the starlets to popularize the iconic 1920s bob!
She's like the deep cut version of Louise Brooks, with majority silent films, and a large percentage of them lost-- BUT 'Why Be Good?' is such a fun movie and she wears really cute dresses and has all the best parts of Pre-Code leading lady fun!

92 notes
·
View notes
Text
Berenice Abbott in Philip Johnson’s apartment
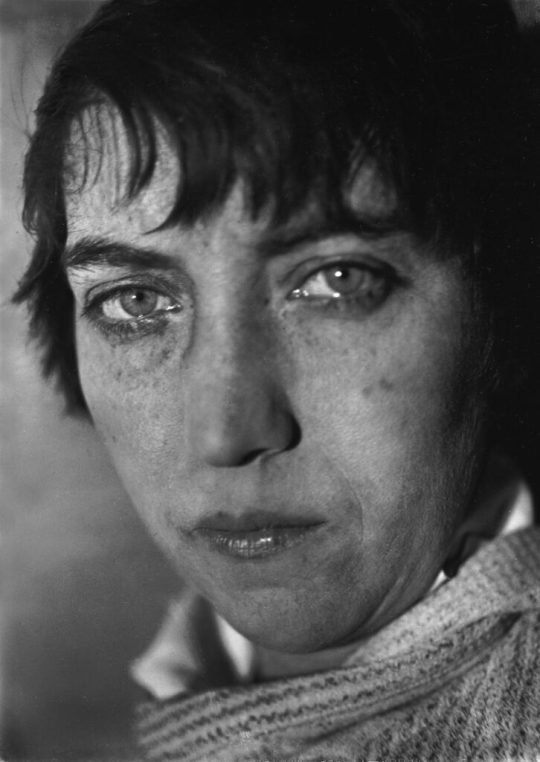
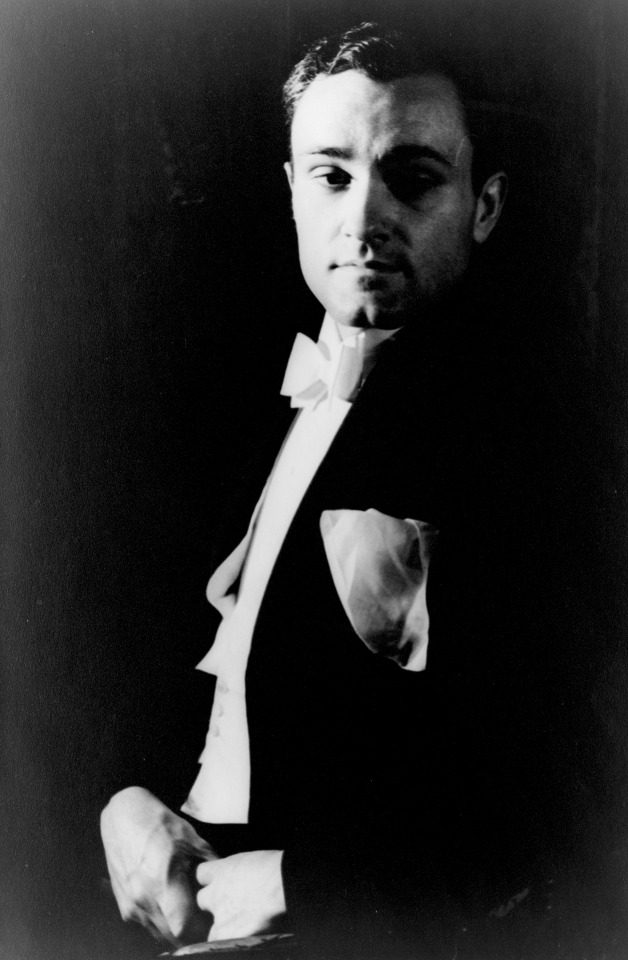


Berenice Abbott, 1930 (Walker Evans) / Philip Johnson, 1933 (Carl Van Vechten)
These portraits are the most obvious choices from this time period and conveniently suggest the biographical contrast between the two: Abbott had been a struggling American artist in Paris, an assistant to Man Ray, but she later established a portrait business, built a reputation and gained a steady flow of sitters. In January 1929, at age 30, she left for New York.
Abbott departed on the ship from France with the archive of Eugène Atget: 17 crates according to the Julia van Haaften's biography. She naively thought selling Atget prints and licensing would provide a healthy income.
The new architecture of the city enthralled her and Abbott quickly began to conceive and photograph a topographic survey of the city. By fall 1929 the stock market had crashed, the Great Depression had begun and the portrait business was no longer promising. Abbott wanted to charge $150 a portrait, at a time when you could get one done for a dollar. This environment forced her to change business models, looking for patrons for the New York project.
Abbott first encountered Philip Johnson in New York in 1931, at the “Rejected Architects” exhibit, a salon des refusés for modern architects and an early introduction of the International Style to New York.
Johnson was a 25-year-old who came from inherited wealth. Rachel Maddow’s "Prequel: An American Fight Against Fascism" suggests his portfolio produced, in today’s dollars, from $240,000 to $1.2M in dividends a year. His financial backing of the architecture department at MOMA resulted in him becoming director of that department. He had discovered Mies van der Rohe on one of his traipses across the continent and was eager to bring the new style to New York. While Johnson was financially very comfortable, he had unsatisfied ambitions, larger than being a curator of architecture and beyond architecture itself.
In 1932 Abbott was part of MOMA’s Murals by American Painters and Photographers exhibit, which Johnson certainly would have been aware of, if not directly involved in, as the point of the show was large modern murals for architecture projects such as Rockefeller Center in the form of seven by twelve foot murals. Greg Allen has the backstory on that exhibit (since his 2010 post the full catalog with her photos has been published on the MOMA site).
For her New York survey, Abbott was looking for $18,750 ($390,000 in today’s dollars), enough to fund a year long project, travel, a car with two full time assistants to deliver 350-500 prints and negatives. Johnson did not financially support Abbott’s New York project, nor did the museum sponsor it, but he offered a strong letter of recommendation, on MOMA letterhead: "You have a deep love for New York, you are an excellent photographic technician and you have the artistic power of selecting the essential."
The goal was to find 75 patrons among the wealthy MOMA donors to contribute $250 each. Despite Johnson’s endorsement, this fundraising effort was a flop. It would take her until 1940 to finish it, but "Changing New York" became one of the great photographic projects of the 20th century.
Van Haaften describes an architecture and photography exhibition Johnson and Abbott planned to do together, called "America Deserta," about the visual repercussions of the Depression. It sounds like an early version of what we now call "ruin porn." She writes that Johnson could have financed the project out of his own pocket, but neither he, nor the museum, pulled the trigger. (Decades later, architecture critic Reyner Banham wrote an excellent book about the actual desert titled "Scenes in America Deserta")

Johnson was doing interior design in New York for friends and acquaintances, hoping the examples of his work could help establish him (and the International Style he had signed on with). An early project was for MOMA’s Alfred Barr. Mark Lamster writes in "Man in the Glass House" that Barr couldn’t afford the real Mies furniture that Johnson had already acquired for himself, so Johnson designed knock-off tubular chairs.

cover of Arts and Decoration, September 1933, from the Burlingame, California library via archive.org
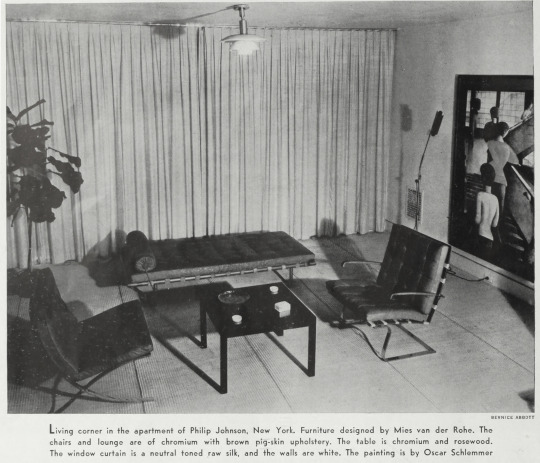
Johnson’s own apartment was his first top-to-bottom interior design project. He was eager, bordering on desperate to get paying clients, to establish himself. He didn't need the money, but wanted clients as a stamp of approval from the New York elite, like the Rockefellers. He enlisted Abbott to take photos to premiere it in Arts and Decoration magazine.

The International Style had already taken root in Los Angeles, but New York was not ready for what he was offering. Perhaps Abbott’s photos of his apartment are part of why the new thing seemed unconvincing. Starting with the watercolor cover or paging through this magazine aimed at the wealthy, the features contrast traditional style versus examples of the new style.
If you've never been in a modern interior before and these photos are your first glimpse, it's not appealing. Johnson was no Neutra and he had not found his Julius Shulman. The magazine's reproduction quality of the photography is not good. Abbott's photographs feel cramped. The lighting is a combination of murky corners and distracting shadows. The styling, a fiddle leaf fig, the place settings at the dining table, feels forced.

In terms of art history, the most interesting of Abbott's photographs features a painting directly from the Bauhaus. It's Oskar Schlemmer's Bauhaus Stairway (1932). Lamster outlines the very messy deal that brought the painting to New York. In March 1933 Barr asks Johnson to buy it, unseen, thinking it will end up at MOMA. As the Nazis breathe down Schlemmer's neck for being a "degenerate artist," Johnson sends a telegram offering a price, but then claims a typo added a zero and pays 10x less. This dispute isn't resolved until after the year 2000. Johnson keeps the painting in his collection for another ten years.

the captions drop the "e" Abbott had added to her name (Bernice vs Berenice).
What explains the vast difference between the great photos Abbott is making on the streets of New York and these mediocre interiors? She creates "Exchange Place" the same year. Spending time with Abbott’s archive on NYPL and Getty looking for interior photos to compare to these photos of Johnson's apartment to, left me with another question: Why are photographs of interiors uncommon until the 1940s? In her Paris portraits the interior of her studio plays a significant role as background.
Van Haaften writes that Abbott is using two cameras in these early years in New York:
5x7 inch view camera (with reducing back to 12x9cm, which is a large “medium format” negative )
Graflex that she acquired to do portraits of Guggenheim children (probably a 4x5 inch press style camera).
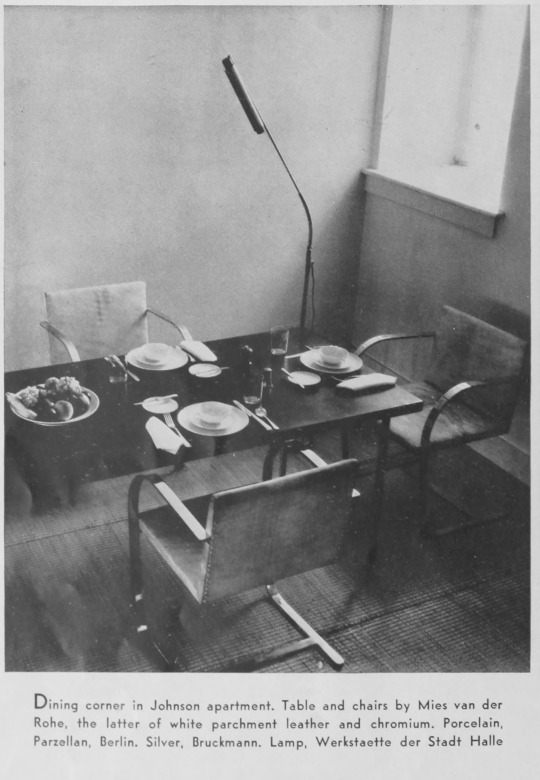

Abbott is on a ladder to make the photographs of Johnson's place and perhaps the combination of lens focal length and the size of the apartment presented a challenge in creating enough space. It’s possible, despite the two cameras, that she simply didn’t have a wide enough lens to do interior work at a time when lenses were expensive and money was tight. Or that she didn’t prefer to use spotlights or flash. Perhaps her focus was so intense on the exterior of the city that she rarely set up the camera indoors.
For Johnson, it’s possible to imagine if New York had been more open to the new style, if the magazine caused a stir, if he was encouraged to become an architect at this moment, his descent into fascism would have never happened. After the photos are published in the September 1933 issue, 1934 is a rollercoaster year for Johnson: he has a breakout hit of an exhibit in Machine Art (March-April). But by December, he quits MOMA to focus on his fascist party. He’s 28 years old. His pursuit of the fantasy of a domestic version of Nazism brings him to Germany, to cheer on the invasion of Poland. Lamster writes that he only to returns to architecture in 1941, when it’s clear that he has barely escaped being charged with treason. He goes from being a millionaire who shipped his own car to Europe for his Nazi tour to cleaning Army toilets.
Van Haaften’s biography of Berenice Abbott is not specific about when Abbott broke off her friendship with Johnson. We can assume it happens sometime between the apartment photoshoot and Johnson leaving MOMA. Abbott was a communist or socialist for most of her life and American Nazis like Johnson were very clear on what they would do to communists if they gained power. Van Haaften writes: "the two friends later parted ways over Johnson’s political views and his enthusiasm for the Third Reich." The book's footnote indicates the source for this is her 1993 phone interview with … Philip Johnson.
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing Analysis: Cannery Row (Cultural References)

John Steinbeck’s Cannery Row (1945) opens with the following declaration:
“Cannery Row in Monterey California is a poem, a stink, a grating noise, a quality of light, a tone, a habit, a nostalgia, a dream” (1).
Set in a fictionalized version of Cannery Row in Monterey, California, Steinbeck uses his cast of homeless people, drunks and prostitutes to express profound truths about humanity.
Abacus (6): A counting device that was used before the creation of calculators.
Belles-lettres (64): A type of literary work, one that is usually expressed in essays, poetry and deals with intellectual subject matter.
Beret (123): A soft hat that has no bill and no brim. Often worn in the military.
Billings, Josh (61): The pen name for Henry Wheeler Shaw, a respected humorist of the 20th century.
Black Marigolds (171): A poem written by E. Powys Mathers.
Bloomer League (140): A baseball league that was comprised primarily of women that started during the early 1900’s.
Carborundum (90): Another name for silicon carbide, which is the sole chemical compound of carbon and silicon.
Chalmers (154): A type of car that was created and sold during the early 1900’s.
Chorea (144): An illness that causes involuntary movement in various parts of the body.
Collier’s (magazine) (139): Founded by Peter Collier, Collier’s Once a Week debuted in 1888 and went on to become one of America’s most popular magazines.
Count Basie (114): A prominent figure during the swing period of jazz, as well as a good example of big band style.
Dadaist (122): An artist or a writer who practiced Dada, a movement that rejected traditional art and contemporary culture.
Daisy Air Rifle (104): A brand of rifle created by the historic Daisy company.
Distemper (134): An infection in dogs that can be diagnosed through symptoms of a runny nose, poor appetite, and coughing.
“Fighting Bob” (111): A reference to Robert M. La Follette Sr. fight against Washington and other politicians who choose to enter WWI.
Ford Model T (61, 106): A truck built by Ford Motor Company.
The Great Depression (16): A result of the 1929 stock market crash, which left many Americans without money or jobs.
Great Fugue (163): A musical work by Beethoven.
Goiter (97): The enlargement of the thyroid gland.
Influenza (89): An infection more commonly known as the “flu.” It was responsible for claiming the lives of millions worldwide before effective vaccines were created to treat and prevent it.
Knights of Columbus (130): A Catholic organization that seeks to aid family members within the organization who are in financial need.
Knights Templar (130): A group of knights who originated in Jerusalem during the year of 1119. Though shrouded in mystery, the Knights Templar are believed to have protected the Holy Grail.
Laudanum (107): A mixture of opium and derivatives of alcohol.
Masonic Lodge (104): A meeting place for Freemasons or former Freemasons.
Mastoids (89): The skull bones that house the ear.
Mastoiditis (90): Mastoiditis occurs when an infection in the middle ear spreads to the mastoids and then causes an infection that produces fevers and headaches.
Monteverdi’s Hor ch’ el Ciel e la Terra (119): A song by the Italian musician Claudio Monteverdi, who lived in the 16th and 17th century.
Novena (88): A prayer that is said over a nine-day period that requests a special favor from God.
“Panama Pacific International Exposition of 1915” (111): The 1915 Worlds Fair that was held in San Francisco, California.
Petrarch (119): A famous writer of the 14th century who is credited with being the founding father of Humanism.
Point Lobos (64): A state reserve on the central coast of California in Monterey County.
Prohibition (72): A move by the United States government to reduce the amount of alcohol consumed in the United States through limiting individuals and businesses who sold alcohol.
Purse Seiners (67): Fishing boats equipped to fish with a purse seine, a kind of fishing net.
“Remember the Maine” (111): The sinking of the U.S.S. Maine, which was the catalyst for the Spanish-American War.
Rimbaud (124): A 19th century French writer who is most remembered for his contribution to the symbolist movement.
Robert Louis Stevenson (61): A Scottish author who is most famous for works such as Treasure Island and The Black Arrow.
Saturnalia (112): The week of December 17th-23rd during which a feast was held by the Romans to celebrate their dedication Saturn’s temple.
Scarlatti (129): Last name of Giuseppe Domenico Scarlatti, an Italian harpsichordist born during the 17th century who later moved to Spain and continued to practice music there.
Sculpin (135): A kind of small fish.
St. Francis (of Assisi) (144): A saint in the Catholic church who is known for his great love for God, animals, and the sick.
Treasure Island (64): A book written by Robert Louis Stevenson.
Vaudeville (109): A form of American variety entertainment that marked the beginning of popular entertainment as a lucrative business.
“White Sale” (103): A sale either of household goods, or when a store drastically reduces their prices for a short period of time.
Source ⚜ More: Writing Notes & References
#cannery row#john steinbeck#literature#writing analysis#writeblr#langblr#studyblr#writers on tumblr#writing prompt#poetry#spilled ink#dark academia#writing reference#poets on tumblr#writing inspiration#writing ideas#creative writing#writing inspo#writing resources
27 notes
·
View notes
Text

Matt Wuerker, Politico
* * * * *
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
October 30, 2024
Heather Cox Richardson
Oct 31, 2024
On Friday, October 25, at a town hall held on his social media platform X, Elon Musk told the audience that if Trump wins, he expects to work in a Cabinet-level position to cut the federal government.
He told people to expect “temporary hardship” but that cuts would “ensure long-term prosperity.” At the Trump rally at New York City’s Madison Square Garden on Sunday, Musk said he plans to cut $2 trillion from the government. Economists point out that current discretionary spending in the budget is $1.7 trillion, meaning his promise would eliminate virtually all discretionary spending, which includes transportation, education, housing, and environmental programs.
Economists agree that Trump’s plans to place a high tariff wall around the U.S., replacing income taxes on high earners with tariffs paid for by middle-class Americans, and to deport as many as 20 million immigrants would crash the booming economy. Now Trump’s financial backer Musk is factoring in the loss of entire sectors of the government to the economy under Trump.
Trump has promised to appoint Musk to be the government’s “chief efficiency officer.” “Everyone’s going to have to take a haircut.… We can’t be a wastrel.… We need to live honestly,” Musk said on Friday. Rob Wile and Lora Kolodny of CNBC point out that Musk’s SpaceX aerospace venture has received $19 billion from the U.S. government since 2008.
An X user wrote: “I]f Trump succeeds in forcing through mass deportations, combined with Elon hacking away at the government, firing people and reducing the deficit—there will be an initial severe overreaction in the economy…. Markets will tumble. But when the storm passes and everyone realizes we are on sounder footing, there will be a rapid recovery to a healthier, sustainable economy. History could be made in the coming two years.”
Musk commented: “Sounds about right[.]”
This exchange echoes the prescription of Treasury Secretary Andrew Mellon, whose theories had done much to create the Great Crash of 1929, for restoring a healthy economy. “Liquidate labor, liquidate stocks, liquidate the farmers, liquidate real estate,” he told President Herbert Hoover. “It will purge the rottenness out of the system. High costs of living and high living
will come down. People will work harder, live a more moral life. Values will be adjusted, and enterprising people will pick up the wrecks from less competent people.”
Mellon, at least, was reacting to an economic crisis thrust upon an administration. Musk is seeking to create one.
Today the Commerce Department reported that from July through September, the nation’s economy grew at a solid 2.8%. Consumer spending is up, as is investment in business. The country added 254,000 jobs in September, and inflation has fallen back almost to the Federal Reserve’s target of 2%.
It is extraordinarily rare for a country to be able to reduce inflation without creating a recession, but the Biden administration has managed to do so, producing what economists call a “soft landing,” rather like catching an egg on a plate. As Bryan Mena of CNN wrote today: “The US economy seems to have pulled off a remarkable and historic achievement.”
Both President Joe Biden and Democratic presidential nominee Vice President Kamala Harris have called for reducing the deficit not by slashing the government, as Musk proposes, but by restoring taxes on the wealthy and corporations.
As part of the Republicans’ plan to take the country back to the era before the 1930s ushered in a government that regulated business and provided a basic social safety net, House speaker Mike Johnson (R-LA) expects to get rid of the Affordable Care Act.
At a closed-door campaign event on Monday in Pennsylvania for a Republican House candidate, Johnson told supporters that Republicans will propose “massive reform” to the Affordable Care Act, also known as “Obamacare,” if they take control of both the House and the Senate in November. “Health-care reform’s going to be a big part of the agenda,” Johnson said. Their plan is to take a “blowtorch to the regulatory state,” which he says is “crushing the free market.” “Trump’s going to go big,” he said.” When an attendee asked, “No Obamacare?” he laughed and agreed: “No Obamacare…. The ACA is so deeply ingrained, we need massive reform to make this work, and we got a lot of ideas on how to do that.”
Ending a campaign with a promise to crash a booming economy and end the Affordable Care Act, which ended insurance companies’ ability to reject people with preexisting conditions, is an unusual strategy.
A post from Trump last night and another this morning suggest his internal polls are worrying him. Last night he claimed there was cheating in Pennsylvania’s York and Lancaster counties. Today he posted: “Pennsylvania is cheating, and getting caught, at large scale levels rarely seen before. REPORT CHEATING TO AUTHORITIES. Law Enforcement must act, NOW!”
Trump appears to be setting up the argument he used in 2020, that he can lose only if he has been cheated. But it is increasingly apparent that the get-out-the-vote, or GOTV, efforts of the Trump campaign have been weak. When Trump’s daughter-in-law Lara Trump and loyalist Michael Whatley became the co-chairs of the Republican National Committee in March 2024, they stopped the GOTV efforts underway and used the money instead for litigation. They outsourced GOTV efforts to super PACs, including Musk’s America PAC.
In Wired today, Jake Lahut reported that door-knockers for Musk’s PAC were driven around in the back of a U-Haul without seats and threatened with having to pay their own hotel bills if they didn’t meet high canvassing quotas. One of the canvassers told Lahut that they thought they were being hired to ask people who they would be voting for when they flew into Michigan, and was surprised to learn their actual role. The workers spoke to Lahut anonymously because they had signed a nondisclosure agreement (a practice the Biden administration has tried to stop).
Trump’s boast that he is responsible for the Supreme Court’s overturning of the 1973 Roe v. Wade decision recognizing the constitutional right to abortion is one of the reasons his support is soft. In addition to popular dislike of the idea that the state, rather than a woman and her doctor, should make decisions about her healthcare, the Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization decision is now over two years old, and state examinations of maternal deaths are showing that women are dying from lack of reproductive healthcare.
Cassandra Jaramillo and Kavitha Surana of ProPublica reported today that at least two pregnant women have died in Texas when doctors delayed emergency care after a miscarriage until the fetal heartbeat stopped. The woman they highlighted today, Josseli Barnica, left behind a husband and a toddler.
At a rally this evening near Green Bay, Wisconsin, Trump said his team had advised him to stop talking about how he was going to protect women by ending crime and making sure they don’t have to be “thinking about abortion.” But Trump, who has boasted of sexual assault and been found liable for it, did not stop there. He went on to say that he had told his advisors, “I’m going to do it whether the women like it or not. I am going to protect them.”
The Trump campaign remains concerned about the damage caused by the extraordinarily racist, sexist, and violent Sunday night rally at Madison Square Garden. Today the campaign seized on a misstatement President Biden made when condemning the statement from the Madison Square Garden event that referred to Puerto Rico as a “floating island of garbage.” They tried to turn the tables to suggest that Biden was calling Trump supporters garbage, although the president has always been very careful to focus his condemnation on Trump alone.
In Wisconsin today, when he disembarked from his plane, Trump put on an orange reflective vest and had someone drive him around the tarmac in a garbage truck with TRUMP painted on the side. He complained about Biden to reporters from the cab of the truck but still refused to apologize for Sunday’s slur of Puerto Rico, saying he knew nothing about the comedian who appeared at his rally.
This, too, was an unusual strategy. Like his visit to McDonalds, where he wore an apron, the image of Trump in a sanitation truck was likely intended to show him as a man of the people. But his power has always rested not in his promise to be one of the people, but rather to lead them. The pictures of him in a bright orange vest and unusually dark makeup are quite different from his usual portrayal of himself.
Indeed, media captured a video of Trump’s stunt, and it did not convey strength. MSNBC’s Katie Phang watched him try to get into the truck and noted: “Trump stumbles, drags his right leg, almost falls over, and tries at least three times to open the door…. Some transparency with Trump’s medical records would be nice.”
The Las Vegas Sun today ran an editorial that detailed Trump’s increasingly obvious mental lapses and concluded that Trump is “crippled cognitively and showing clear signs of mental illness.” It noted that Trump now depends “on enablers who show a disturbing willingness to indulge his delusions, amplify his paranoia or steer his feeble mind toward their own goals.” It noted that if Trump cannot fulfill the duties of the presidency, they would fall to his running mate, J.D. Vance, who has suggested “he would subordinate constitutional principles for personal profit and power.”
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#political cartoon#Matt Wuerker#Politico#Heather Cox Richardson#Letters From an American#Las Vegas Sun#MAGA extremism#garbage truck stunt#women's health#reproductive rights#Musk#Affordable Care Act#Obamacare#project 2025#MAGA's plans for you
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
CW: Politics, Human Rights discussion
I Collect BJDs, Too. Trump's Second Term Should Alarm You.
We should all know by now that Trump winning the presidency this year is catastrophic for the basic human rights of minorities in the US (and abroad, let's be completely honest here). He is planning to enact a political playbook of draconian laws meant to 'bring back' a fictional ideal of the US, one that sees everyone subservient to conservative cishet white men. This is not fear-mongering, it is simply a cold hard fact that the people backing him financially have a lot to gain from instilling a form of government that solely caters to their whims and desires, and a lot of the Project 2025 playbook not only gives the power to white men in general over that of women, LGBTQIA+, and BIPOC people within our boarders, but will give power to the wealthy white men in this country who want to own everything, including our very bodies.
This should concern you. I don't know how else to express to you that it should concern you. There are not enough words at my disposal to express just how dire this situation is for all of us. And if you aren't concerned, and you're a BJD collector like I am, then allow me to make it personal so you can understand.
These tarrifs will result in much narrower access to BJDs as a whole. I'll use V0lks as an example: V0lks has a store based in the US, in Los Angeles. They send this store batches of dolls and clothes and wigs and eyes and replacement parts periodically to help keep them stocked. When they run out of a thing (unless that thing was being phased out/replaced/discontinued), the employees make a list of what they need, use their own profits to pay for it, and then Volks would send them new stock to fill the gaps. When the tarrifs take hold, this new stock will be more expensive, since Japan in general will be forced to pay higher import tarrifs. That means the US Volks location will have to spend more money on the restock shipments, which will in turn make the dolls more expensive so that Volks can maintain a substantial profit margin; but these tarrifs will backfire, because a 20%-60% increase will not translate to good profit for Volks, which means the US location will be shuttered to keep Volks from hemorrhaging money, which means your only option would be to buy your dolls from Japan... and you'd be paying the extra shipping money, because it will still cost Volks extra money to ship dolls into the US. This may result in Volks choosing not to ship dolls to the US at all, meaning you won't be able to buy any of their dolls again unless you can find a third party willing to spend their own money to send you these dolls at even higher prices that include the profit THEY need to make for doing so.
Lots of doll companies are not as big as V0lks. A lot of them are considerably smaller. The smaller ones will cease operations in the US entirely right off the bat. Some will hold on, but eventually abandon us as a market. A lot of independant BJD artists in the US will not be able to make and sell their dolls because there are no well known (non-scammer) resin workers who will be able to help create a solid product the way that companies like V0lks or R1ngdoll or Lutz or Minifee can offer. Recast companies will also cease operations in the US, because they still need to import the recasts from the counterfeit suppliers in other countries who won't be able to afford the tarrifs point blank period. So if you thought that recasts would be an option, think again (they shouldn't be one anyway, but that's a different convo that we aren't gonna have right now).
These tarrifs, these policies, will affect vast swathes of non-American products, like snacks, drinks, food, entertainment, and toys. One of the big ones that overlaps with the BJD community, anime and manga, will likely vanish, as it will likely be deemed 'too adult' by the religious extremists in power. You will lose access to these things and you will not have another chance to get them for a very very very long time. By the time you do have the chance, some of the BJD companies whose market focus has been the USA might be completely gone. SmartD0ll, for example: their company relies on US consumption of their products, and they market HEAVILY to the US market because we are a really really easy demographic to market to on the global stage. Danny has staked a LOT of his company into our willingness to buy his extremely westernized anime dolls. They are not very popular in Japan, and he focuses very little on other markets where his negative behavior isn't as readily tolerated. Unless he does a massive pivot to a different market... SmartDolls will be gone. I won't speak on how I personally feel about SmartD0ll, but I know that a LOT of people love his product, and will be utterly devastated when they can never buy them again.
So, if you are in this community and voted for him, you should be worried. I know there are people in this community who did, because I've seen the alarming uptick of conservative rhetoric in this community first hand. At the end of the day, you are probably just as disillusioned with the US government and chose to vote accordingly. Even if that meant voting for a felon who has a vetted interest in toppling our current democratic structures and isolating the US economically and cleansing it ethnically and religiously. You will lose access to your dolls. Be ready for that.
~Anonymous
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cosplay the Classics: Nazimova in Salomé (1922)—Part 2
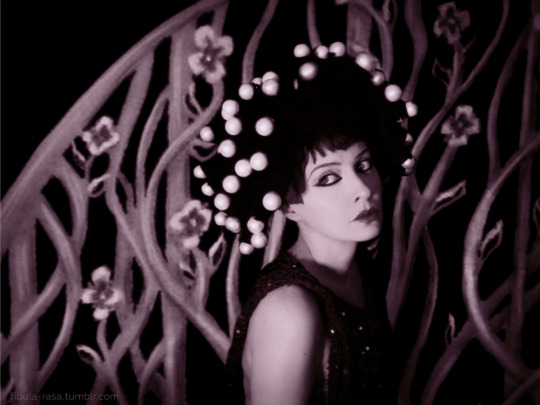

My cosplay of Nazimova as Salomé
As the studio system emerged in the American film industry at the start of the 1920s, many of the biggest stars in Hollywood chose independence. Alla Nazimova, an import from the stage, was one of them. In 1922, she made a series of professional and creative decisions that would completely change the trajectory of her career.
In part one of CtC: Nazimova in Salomé, I described how Nazimova’s independent productions were shaped in response to trends and ideas surrounding young/independent womanhood in America after World War I and the influenza pandemic. Here in part two, I’ll fit these productions, A Doll’s House and Salomé, into the broader context of the big-money business of film becoming legitimate in America.
While the full essay and photo set are available below the jump, you may find it easier to read (formatting-wise) on the wordpress site. Either way, I hope you enjoy the read! Oh and Happy Bi Visibility Day to all those who celebrate!

My cosplay of Nazimova as Salomé
Artists United? Allied Artists and the Release of Salomé
When Nazimova made her screen debut in War Brides (1916), the American film industry was undergoing a series of formative changes. Southern California became the center of professional filmmaking in the US—fleeing New Jersey (where War Brides was filmed) largely because of Thomas Edison’s attempts to monopolize the business. Preferences of audiences and exhibitors shifted away from one and two-reel films and towards feature-length films. The Star System emerged in full force. Nazimova soon relocated to Hollywood, signed a contract with Metro, and reaped the benefits of this boom period for American film artists.
The focus on feature-film production and the marketing of films based on the reputations of specific filmmakers or stars required a greater initial outlay of resources—time, money, and labor. But, it also paid dividends—the industry quickly grew into a big-money business. The underlying implication of that is that a larger share of the profits were shifted from the people doing the creating (artists and technicians) and towards other figures (capitalists). In practice, this also meant film companies would become eligible for listing on the stock exchange and could secure funding from banks and financial institutions, both of which were rare or impossible before the mid-1920s. The major players on the business end of production, distribution, and exhibition, therefore, wanted to consolidate their power and reduce the power and influence of the filmmakers.
To illustrate how momentous this handful of years was in the history of the US film industry, allow me to highlight a few key events. Will Hayes’ office was set up in 1922 to make official Hollywood’s commitment to self-censorship. Eastman Kodak introduced 16 mm film in 1923, a move which, while making filmmaking more accessible and affordable, also widened and formalized the division between the professional industry and amateur filmmaking. Dudley Murphy’s “visual symphony” Danse Macabre[1] was released in 1922—considered America’s first avant-garde film. Nazimova’s Salomé was considered America’s first art film from its initial release in 1923. That these labels were deemed relevant in this period illustrates the line being drawn between those films and film as a conventional, commercial product. The concept of art cinemas in the US was first proposed in 1922 spurring on the Little Cinema movement later in the decade.

from Danse Macabre

from Salomé
As any industry matures, both the roles within it and its output become more starkly delineated. That is to say that, as the US industry began differentiating between art/avant-garde/experimental film and commercial film, the jobs within professional filmmaking also became more firmly defined. Filmmaking has always been a collaborative art, but in the period prior to the 1920s, it was common for people in film to do a little of everything. As a result, what sparse credits made it onto the final film didn’t necessarily reflect all of the work that was done. To illustrate this using Nazimova,[2] at Metro, she had her own production unit under the Metro umbrella. While her films were “Nazimova Productions,” she didn’t have full creative control of her films. However, Nazimova did choose her own projects, develop said projects, and contribute to their writing, directing, and editing. When those films were released, aside from the “Nazimova Productions” banner, her only credit would usually be for her acting. Despite that impressive level of creative power, the studio still had the ultimate say on whether a film got made, and how it would be released. As studios grew and tightened control of their productions, this looser filmmaking style became much less common.
The structure of the industry at this time was roughly tripartite—production, distribution, and exhibition. Generally speaking, the way studio-made films traveled from studio to theatre—before full vertical integration—was that the production company would make available a slate of films of different scales. (Bigger productions with bigger names attached would have a special designation and come with higher rental fees.) Famous Players-Lasky was the biggest production house at the time, though other studios, like Metro, were quickly catching up. Distribution companies would then place this slate of films on regional exchanges, centered in the biggest cities in a given region. Exhibitors (this could be owners of chains like Loew’s in the Midwest and Northeast, the Saengers around the gulf coast, or individual theatre owners) could then rent films through their local exchanges. (This was an ever-shifting industry, so this process was not true for every single film. This is only meant as a quick overview of the system.) As the 1920s wore on, exhibitors began entering the production arena and producers further merged with distribution companies and exhibition chains. Merger-mania was the rule of the day.

My cosplay of Nazimova as Salomé
As merger upon merger took place and a handful of businessmen tried to monopolize the industry, American filmmakers responded by championing the artistic legitimacy of filmmaking in the US. Leading this charge were the very filmmakers on whose backs the big business of film had been built. As noted in Tino T. Balio’s expansive history of United Artists, The Company Built by the Stars:
…Richard A. Rowland, president of Metro Pictures, proclaimed that ‘motion pictures must cease to be a game and become a business.’ What he wanted was to supplant the star system, which forced companies to compete for big names and pay out-of-this-world salaries for their services. Metro, he said, would thenceforth decline from ‘competitive bidding for billion-dollar stars’ and devote its energies to making big pictures based on ‘play value and excellence of production.’”
It’s notable for us that these ideas were espoused by Rowland, head of the studio where Nazimova was currently one of those “billion-dollar stars.” (“Billion-dollar” is obviously a massive overstatement.) It was a precarious time for any filmmaker who cared about the quality and artistry of their work. It was this environment that birthed United Artists, a new production company built around the prestige and reputation of its filmmakers, Douglas Fairbanks, Mary Pickford, Charlie Chaplin, and D.W. Griffith. As the statement announcing the formation of UA detailed:
“We also think that this step is positively and absolutely necessary to protect the great motion picture public from threatening combinations and trusts that would force upon them mediocre productions and machine-made entertainment.”
It’s an accurate assessment of industry trends at the time. If the desired product is a high-quality feature-length film, production is necessarily more expensive. As the UA statement intimates, monopolizing the entire industry and sacrificing quality for quantity to fill the exchanges and theatrical bills was the studio heads’ solution to rising costs. Not a great signal for filmmaking as art in America.

My cosplay of Nazimova as Salomé
So, Nazimova was in good company when she chose to go independent, believing in film as art and that American moviegoers deserved better than derivative, studio-conceived films. Some of the other artists who went independent included George Fitzmaurice (one of the most revered directors of the silent era, though most of his films are now sadly lost), Charles Ray, Max Linder, Norma Talmadge (in alliance with Sam Goldwyn), and Ferdinand Pinney Earle (whose massive mostly-lost artistic experiment Omar Khayyam, I profiled in LBnF). If these filmmakers shared the motivation of UA to create higher-calibre productions, where would the money come from? For Nazimova, the answer was her own bank account.
In 1922, Nazimova’s final film for Metro, Camille (1921), was still circulating widely due to the rising popularity of her co-star, Rudolph Valentino, after the release of Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse (1921) and The Sheik (1921). While Nazimova had the funds to complete A Doll’s House and Salomé, there was no sure bet for the films’ releases. Nazimova’s initial concept for her independent productions was the “repertoire” film. This scheme would have seen A Doll’s House released as a shorter film with Salomé as a feature and the two could be rented as a package by exhibitors. It was a creative response to growing tensions between producers and exhibitors over a practice called block booking. Block booking was a strategy studios employed to leverage the Star System to its fullest. They would take the most in-demand films associated with the biggest drawing stars and only make them available in a package deal with productions that were perceived as less marketable. Nazimova was aware that her films at Metro had been rented this way (as the special feature). It’s not completely clear from my research if the decision to release Salomé and A Doll’s House as two features was creative, practical, or a combination of the two. The “repertoire” concept may not have gone according to plan, but it was an early indication that Nazimova was well-informed of the nuances of distribution and exhibition.
Nazimova’s need for proper distribution was met by United Artists’ distribution subsidiary, Allied Artists. United Artists’ first few years were a struggle. Fairbanks, Pickford, and Griffith[3] needed significant time and money to finish the high-quality productions that they promised and Allied was their solution. This distribution arm would release the work of other independent talent using the same exchanges as UA, but under a different banner. Though Allied used UA’s exchanges for distribution, the subsidiary had its own staff. Allied having different branding would also protect the prestige of the UA name. (An unkind, but not entirely inaccurate summary: the money your work brings in is good enough for us, but your work is not.) Allied would have a full release slate to generate the revenue that UA needed to remain in operation.
Nazimova was one of the filmmakers who signed a distribution deal with Allied and had reason to regret it—though she and Charles Bryant didn’t openly rag on UA/Allied.[4] Notably, Mack Sennett had arranged the release of Suzanna (1923) through Allied and was vocal about the company bungling its release. Differences over distribution and exhibition would also lead to Griffith’s exit from the company and a major rift between Chaplin and Pickford-Fairbanks. After 1923, Allied reduced its operation, at least in part because of the bad reputation they were garnering with other filmmakers. Despite numerous independents losing money on productions released through Allied, by 1923, Allied had netted UA 51 million dollars in revenue!

Trade ad for Salomé from Motion Picture News, 10 March 1923
The questionable deals that these independent filmmakers received with Allied are often mentioned in discourse about the period, but very, very rarely does anyone offer details of what Allied’s inadequate distribution looked like. Using the information available to me via Lantern, I collected and analyzed data regarding the release and exhibition of Nazimova’s final two Metro films and both of her Allied films.[5] Looking at the trade publications Exhibitor’s Trade Review, Moving Picture World, Motion Picture News, and Exhibitors Herald, I categorized every item I found about the release or exhibition of Billions (1920),[6] Camille, A Doll’s House, and Salomé. The “release” items are primarily advertisements, reviews, and news items about release dates or pre-release screenings. The number of these items for all four films were comparable.
The items in the “exhibition” category, however, reveal a marked difference between the Metro and Allied releases. This category includes items like first-run theatre listings, exhibitor feedback, and advertising advice for theatre owners. Only counting exhibition items from the first two years (24 months) from the initial release of each film, Billions and Camille had twice as many items as A Doll’s House and Salomé!
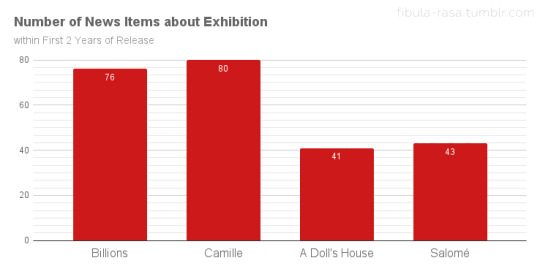
While this isn’t necessarily hard data on how many theatres ran each film, it is a rough indicator of how well the films circulated. This data suggests that neither A Doll’s House or Salomé had distribution comparable to the Metro films. In order to compensate for the Rudy factor—Valentino’s major rise to stardom in 1921—which could have affected Camille’s numbers in a big way, I included Billions as well. Billions was sold as a special (a bigger production with premium rental fees) on Nazimova’s name alone. It was not especially well received. Exhibitors/theatre owners had mixed feelings on the film because Nazimova’s previous film, Madame Peacock (1920), had underperformed. Many exhibitors viewed Billions as an improvement, though it still did not meet their perception of Nazimova’s standard of quality. Despite that, Billions had 76 exhibition-related items across its first 24 months of availability to Camille’s 80.
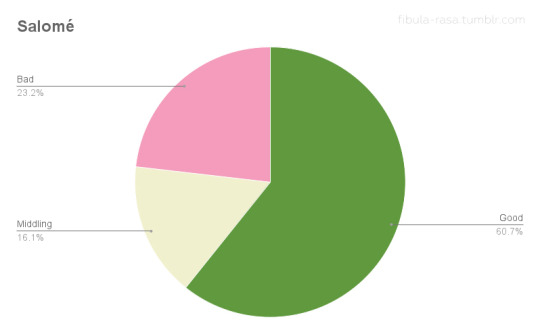
To get a little deeper into this data, I wanted to see how the feedback from exhibitors and theatre owners compared. I broke down the exhibitor feedback for each film as positive, middling, or negative based on how the exhibitors assessed audience response and/or box office receipts. (I discounted feedback that only reflected theatre owners’ own personal assessment of the films without mention of their patrons or receipts.) Positive feedback could be good reception and/or good receipts, middling suggests only average business and no noteworthy reception, and negative indicates poor response and/or poor ticket sales. Since there are so many more items about Camille and Billions than A Doll’s House and Salomé, I compared ratios as an indicator of exhibitor satisfaction. The results were truly surprising.
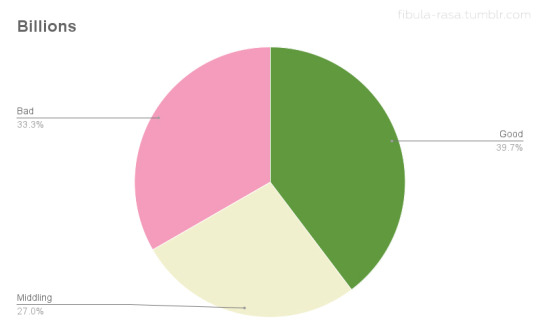
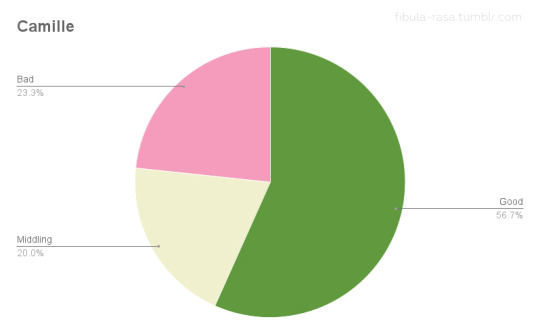
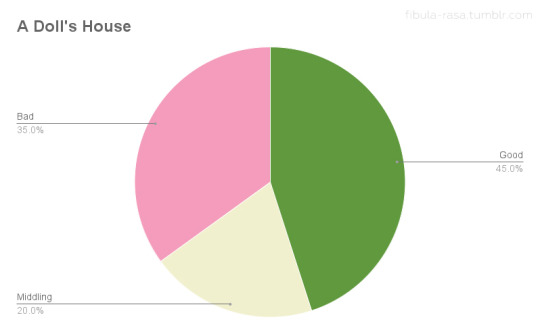
Theatre owners who rented Salomé may have been in significantly smaller numbers than those who ran Camille, but their satisfaction with ticket sales and audience feedback was roughly equivalent. (Though slightly more positive for Salomé!) The numbers for Billions line up with the qualitative assessment I summarized above, displaying a roughly equal 3-way split. A Doll’s House was the most divisive with the highest proportion of negative feedback of the four films, yet with a higher proportion of positive feedback than Billions.
Taking all of this into account, it’s clear that Salomé did not flop because it was too artsy or esoteric for the American moviegoing public. Such assumptions are obviously not very thoughtful or informed by reliable data.[7] A more historically sound reading is that, as professional filmmaking matured into a “legitimate” industry in the US, the various arms of the business were rigidly formed to fit conventional output. The conservatism that this engendered made the American industry ill-equipped at marketing anything too unconventional or experimental. While Hollywood insiders were lamenting European filmmakers artistically outdoing Americans—especially following the US release of The Cabinet of Dr. Caligari (1920)—very few people with the power to shape the industry did anything to support experimentation. Given this environment, Salomé could only have been produced independently, but the quickly ossifying distribution and promotional systems didn’t have the range to give it a proper release. Two films contemporary to Salomé, Beggar on Horseback (1925) and The Old Swimmin’ Hole (1921) offer further evidence of the industry’s limitations.
The Old Swimmin’ Hole is a feature-length production by Charles Ray, experimental in that it uses no intertitles. The story is simple and familiar with Ray playing the Huck-Finn-type character he was well known for. Ray’s experiment was not an expensive one and the film was successful. However, decision makers at First National, the film’s distributors, felt that The Old Swimmin’ Hole was simply too complex for small-town Americans to comprehend and it wasn’t released outside of cities. To put it plainly, the distributor’s unfounded concept of ignorant yokels meant that a film about country living was largely inaccessible to anyone actually living in the country. Though the film was well received and turned a profit, this distribution decision likely limited its audience as well as possible revenue from small-town exhibition.

Stills from The Old Swimmin’ Hole from Motion Picture Magazine, April 1921
Beggar on Horseback was produced by one of the biggest studios in Hollywood, Famous Players-Lasky, and distributed by Paramount. Starring comedian Edward Everett Horton, Beggar was an expressionist comedy based on a popular play. The film had a popular star, popular source material, and was made and released by a major company, but Beggar was apparently too unconventional for that major company to adequately market it. (Unfortunately, only a few minutes of the film survive, so we can’t fully reassess it unless more is found/identified!)

Stills from Beggar on Horseback from Picture-Play Magazine, August 1925
With all these complicating factors at play, how might have Salomé found its audience in 1922-3? Nazimova and Charles Bryant had innovative ideas for the film’s release that might have done the trick, if they had been able to act on them. Nazimova and Sam Zimbalist had finished cutting Salomé in late-spring 1922. Having spent practically all of her money to finish the film, and following A Doll’s House’s disappointing results, Nazimova was eager for Salomé to hit theatres. Though the film was in the can and private preview screenings had been held by Bryant by summer ‘22, Salomé wouldn’t be released until February of 1923. In studio filmmaking, holding a film in extended abeyance wasn’t ideal but it was not disastrous. Studios had significantly more resources and revenue streams than independent producers. If, for example, the release of Billions had been delayed for seven months, Nazimova still had two films on the Metro exchanges (and therefore in theatres) and Camille would have entered production in the meantime. But for Nazimova as an independent producer, this situation was wholly untenable. (In fact, Pickford, Fairbanks, and Griffith were in a similar untenable situation when they founded Allied.)
Initially, Bryant proposed roadshowing Salomé. Roadshowing is a release strategy for notable film productions where a film is toured around major cities, often with in-person engagements by stars, writers, and/or directors. Nazimova expanded the idea of touring with Salomé not simply as a roadshow, but paired with a short play in which she would star. Double the Alla, double the fun. As far as I can tell, there isn’t publicly available information about why Salomé wasn’t roadshowed. However, we do know that Griffith, as the only non-performer in UA, wanted to utilize different approaches for the release of his films—like roadshowing—and it became one of the major points of disagreement with his fellow UA decision makers. That could be taken as an indication that something similar might have occurred with Nazimova and Allied.
As time dragged on without a release date for Salomé and Nazimova returned to theatrical work—openly admitting to audiences that she was broke—Bryant took matters into his own hands. At the end of December 1922, Bryant negotiated with the owner of the Criterion Theatre in New York City for Salomé to run on New Year’s as a special presentation. In two days, Salomé grossed $2,630, setting records for the theatre. Adjusted for inflation, that’s $48,988.96. It was successful enough that the owner of the Criterion opted to hold the film over. This bold move must have lit a fire under Allied’s tuckuses, as Salomé finally had its first-run release a little over a month later.
In the 1920s, the first-run booking of a film was a crucial part of its further success. Concurrent nationwide release of films wasn’t the norm yet, and if a film was a big production, getting booked at high-capacity motion picture houses in major cities was a necessity. These big city releases would, in theory, generate interest in the film with exhibitors across the country and internationally. Basically, if you spent a lot on a movie but couldn’t land a first-run release, you weren’t likely to turn a profit or even break even. Salomé had a handful of first-run bookings and local reviewers from those cities believed the film would succeed. A reviewer from the Boston Transcript in February 1923 wrote:
“…this newest Salome is something far better than a photographed play. Considered both as picture acting, and as an interesting experiment in design, “Salome” is a notable production. It will have a far and wide reaching influence on future films in this country.”
But, as I mentioned, only a handful of first-run theatres played Salomé, and, taken collectively, the notices I analyzed from contemporary trades imply that it didn’t gain traction once it was made available beyond its initial run.

My cosplay of Nazimova as Salomé
During this regrettably short theatrical run, exhibitors and reviewers from trade publications advised that Salomé was a unique film that called for unique promotion. The overall assumption was that theatre owners knew their patrons and recognised whether out-of-the-ordinary movies were popular with them. Rather than purely judging a film’s quality, exhibitors and trade reviewers had concerns specific to exhibition when providing feedback. These concerns cannot be overlooked if you want to understand their assessments. For example, exhibitor feedback was very often informed by how high the rental fees were for a film, even if exhibitors don’t directly mention said fees. That is to say, a mediocre film might be rated highly if the rental fees were modest (and if block booking wasn’t an issue). Reviewers in the early 1920s, both for popular magazines and trade publications, were already accustomed to the formulaic nature of most studio output. Their reviews commonly expressed fatigue with studio films’ lack of originality. And, perhaps surprisingly, this sentiment was shared among theatre owners as well—particularly when a run-of-the-mill film was sold to them as anything other than a “programmer” (a precursor to B-movies).
What I have learned, not just by analyzing feedback for Salomé, but also for all of the films in my LBnF series, is that when a 1920s reviewer calls out bizarreness in a film, it’s not always a negative quality, even when the review isn’t positive. In the case of reviews written for exhibitors/theatre owners, focussing on what makes a movie different is purely pragmatic. It guides how exhibitors might market films to patrons and helps exhibitors judge if a film would be suitable for their audiences. And, from that same research, I’ve found significant indications there were numerous markets throughout the US that were hungry for novelty—contrary to what studio apparatchiks wanted to admit. So, pointing out Salomé’s bizarreness was a recommendation for those markets to consider renting it as much as it was a warning against renting for theatre owners who only had success with more conventional films.

Cover of the Campaign Book for Salomé reproduced in Exhibitors Herald, 9 February 1924
In the case of Salomé, reviews and feedback upon its release focused on two major points:
The film isn’t “adult” in nature. Well-known productions of Strauss’ opera and the 1918 Theda Bara film of the same name led to a presumption of salaciousness. (I talked a bit about that in Part One!)
The film deserves/requires a build up as an artistic event film.
Nazimova’s company helped exhibitors with the latter point in a few ways. The company provided Aubrey Beardsley inspired art posters conceived by Natacha Rambova and executed by Eugene Gise. They printed a book to guide promotion of an artistic spectacle. (So far, I haven’t been able to find a physical or digital copy, so I can’t assess how good the advice was!) Salomé was also distributed with an official musical score, apparently written for a full orchestra.

Art Posters designed by Rambova and painted by Gise as reproduced in Exhibitor’s Trade Review, 10 February 1923
The exhibitors who ran Salomé—and put at least some of this advice into practice—were satisfied with the business it did. By these accounts, the American moviegoing public was attracted by the novelty of Salomé, but what chance were they given to see it?
While this evidence of Allied’s poor distribution work may be circumstantial, it certainly complicates the narratives that Salomé was an unqualified flop or that average Americans weren’t (or aren’t) receptive to artistic experimentation. Given that Nazimova was not the only independent filmmaker who suffered from Allied’s inept distribution, it does seem like the underwhelming business Salomé did was due more to a poor choice of business partners than to any quality of the film or of American moviegoers. That said, with the increasing monopolization of the industry, Nazimova did not have a wealth of options.
Though Salomé was made and released at an tumultuous period for the US film industry, it did eventually find its audience through circulation in art cinemas. As the gap between experimental/avant-garde film widened in the US and the professional industry became less and less tolerant of departures from convention, Americans concerned with film as an art form rallied around amateur filmmaking clubs and art cinemas began popping up in cities by the middle of the decade. Salomé played in these theatres even after the advent of sound—occasionally even today. This is likely the key reason that Salomé survives and we’ve been able to continue to enjoy and reevaluate it one hundred years later.
Salomé is a significant film made at a significant moment in American film history. Nazimova took a major risk in going independent and personally funding two artistic projects. These films were founded on the beliefs that American moviegoers wanted art made by human beings with unique imaginations, feelings, sensibilities and that there was an audience for more than derivative, “machine-made” film. In my opinion, through close analysis of the circumstances of Salomé‘s release, we can see that Nazimova was likely correct, but didn’t get a genuine chance to prove it in her lifetime. Additionally, it’s important to note that Nazimova’s risks did not “ruin” her as is occasionally said. The state of her finances were more greatly affected in the 1920s by her fake husband’s habit of spending her money and by getting swindled by a pair of con artists over her estate, The Garden of Alla. Soldiering on, Nazimova continued to work in both theatre and film for the rest of her life and found more stability with the partner she would meet at the end of the 1920s, Glesca Marshall.
——— ——— ———
Once I finished this “Cosplay the Classics” entry, I realized that it would way too much for me to include a section on another relevant topic to Salomé: Orientalism in Hollywood. But, I feel that the topic is too important to just edit that writing out. Look out for a shorter “postscript” entry soon!
——— ——— ———
☕Appreciate my work? Buy me a coffee! ☕
——— ——— ———
Footnotes:
[1] Danse Macabre is also thought to be a major influence on Walt Disney animating to music, as seen in “Silly Symphonies” and later Fantasia (1940) and Disney’s other musical anthology features. It was also in this period that Disney fled from his debtors in the Midwest to California with his first “Alice” movie. However, the wide-ranging effects of Disney’s business practices were not felt until much later, so that’s another story for another time!
[2] Nazimova was one of a handful of women in Hollywood at the time who held significant creative power. June Mathis and Natacha Rambova, both of whom Nazimova regularly worked with, Mary Pickford and her regular tag-team partner Frances Marion are among some of the others.
[3] Chaplin wouldn’t produce a film for UA until 1923’s A Woman of Paris, as he was fulfilling a pre-existing contract with another studio.
[4] According to Gavin Lambert’s biography of Nazimova (which I discussed as a largely unreliable source in Part One), Robert Florey supposedly advised Nazimova against signing with them, citing Max Linder and Charles Ray as artists who had been “ruined” by their deals. However, the timeline does not quite match up. Though Florey did visit the set of Salomé, Nazimova had already signed the Allied deal by then and Ray had not finished The Courtship of Miles Standish (1923) when Salomé was in production. In fact, there was almost a year and a half between the completion of Salomé and the release of Standish. Whether this was a lapse of memory by Florey or misreporting by Lambert, I can’t be sure.
[5] Originally, I wanted to include Madonna of the Streets (1924) in my comparisons but, at the moment, Lantern has gaps in their Moving Picture World archive for 1924-5. I didn’t want to draw conclusions from incomplete data.
[6] Billions was also a Rambova-Nazimova collaboration. Rambova designed a fantasy sequence for the film.
[7] A mindset that’s still common among commercial media outlets today unfortunately. I could rant and rant about “content” and “content creation” all day but that’s another story for another time.
——— ——— ———
Bibliography/Further Reading
(This isn’t an exhaustive list, but covers what’s most relevant to the essay above!)
Lost, but Not Forgotten: A Doll’s House (1922)
“Nazimova in Repertoire” in Motion Picture News, 29 October 1921
“Alla Nazimova Plans for Her New Pictures” in Moving Picture World, 29 October 1921
“Nazimova Abandons Dual Program for Latest Film” in Exhibitors Herald, 24 December 1921
“Plays and Players”in Photoplay, February 1922
“PICTORIAL SECTION” in Exhibitors Herald, 4 February 1922
“New Nazimova Film May Be Roadshowed“ in Exhibitors Herald, 15 April 1922
“Newspaper Opinions” in The Film Daily, 3 January 1923
“Splendid Production Values But No Kick in Nazimova’s ‘Salome’” in The Film Daily, 7 January 1923
“Claims “Salome” Hit New Mark at N. Y. Criterion” in Exhibitors Herald, 27 January 1923
“Salome” in Exhibitors Trade Review, 20 January 1923
“Nazimova in SALOME” in Exhibitors Herald, 27 January 1923
“Nazimova Appeals To Exhibitors In Behalf of ‘Salome’” in Exhibitor’s Trade Review, 27 January 1923
“Novelty Features Paper and Ads for ‘Salome’” in Exhibitor’s Trade Review, 10 February 1923
“SALOME’ —Class AA” from Screen Opinions, 15 February 1923
Nazimova: A Biography by Gavin Lambert (Note: I do not recommend this without caveat even though it’s the only monograph biography of Nazimova. Lambert did a commendable amount of research but his presentation of that research is ruined by misrepresentations, factual errors, and a general tendency to make unfounded assumptions about Nazimova’s motivations and personal feelings.)
Lovers of Cinema: The First American Avant-Garde 1919-1945 ed. Jan-Christopher Horak (most notably, “The First American Avant-Garde 1919-1945” by Horak, “The Limits of Experimentation in Hollywood” by Kristin Thompson, and “Startling Angles: Amateur Film and the Early Avant-Garde” by Patricia R. Zimmermann)
United Artists: The Company Built by the Stars, Vol. 1 1919-1950 by Tino Balio
#1920s#1922#Salomé#salome#nazimova#alla nazimova#film history#cosplay#queer film#silent era#classic movies#film#avant garde#experimental film#cinema#queer film history#silent cinema#1923#classic cinema#american film#women filmmakers#women in film#silent film#classic film#silent movies#bisexual visibility#cosplayers#natacha rambova#united artists#Metro
36 notes
·
View notes
Note
Why do economists need to shut up about mercantilism, as you alluded to in your post about Louis XIV's chief ministers?
In part due to their supposed intellectual descent from Adam Smith and the other classical economists, contemporary economists are pretty uniformly hostile to mercantilism, seeing it as a wrong-headed political economy that held back human progress until it was replaced by that best of all ideas: capitalism.

As a student of economic history and the history of political economy, I find that economists generally have a pretty poor understanding of what mercantilists actually believed and what economic policies they actually supported. In reality, a lot of the things that economists see as key advances in the creation of capitalism - the invention of the joint-stock company, the creation of financial markets, etc. - were all accomplishments of mercantiism.
Rather than the crude stereotype of mercantilists as a bunch of monetary weirdos who thought the secret to prosperity was the hoarding of precious metals, mercantilists were actually lazer-focused on economic development. The whole business about trying to achieve a positive balance of trade and financial liquidity and restraining wages was all a means to an end of economic development. Trade surpluses could be invested in manufacturing and shipping, gold reserves played an important role in deepening capital pools and thus increasing levels of investment at lower interest rates that could support larger-scale and more capital intensive enterprises, and so forth.
Indeed, the arch-sin of mercantilism in the eyes of classical and contemporary economists, their interference in free trade through tariffs, monopolies, and other interventions, was all directed at the overriding economic goal of climbing the value-added ladder.
Thus, England (and later Britain) put a tariff on foreign textiles and an export tax on raw wool and forbade the emigration of skilled workers (while supporting the immigration of skilled workers to England) and other mercantilist policies to move up from being exporters of raw wool (which meant that most of the profits from the higher value-added part of the industry went to Burgundy) to being exporters of cheap wool cloth to being exporters of more advanced textiles. Hell, even Adam Smith saw the logic of the Navigation Acts!

And this is what brings me to the most devastating critique of the standard economist narrative about mercantilism: the majority of the countries that successfully industrialized did so using mercantilist principles rather than laissez-faire principles:
When England became the first industrial economy, it did so under strict protectionist policies and only converted to free trade once it had gained enough of a technological and economic advantage over its competitors that it didn't need protectionism any more.
When the United States industrialized in the 19th century and transformed itself into the largest economy in the world, it did so from behind high tariff walls.
When Germany made itself the leading industrial power on the Continent, it did so by rejecting English free trade economics and having the state invest heavily in coal, steel, and railroads. Free trade was only for within the Zollverein, not with the outside world.
And as Dani Rodrik, Ha-Joon Chang, and others have pointed out, you see the same thing with Japan, South Korea, China...everywhere you look, you see protectionism as the means of achieving economic development, and then free trade only working for already-developed economies.
#political economy#mercantilism#economic development#early modern state-building#early modern period#laissez-faire#classical liberalism#classical economics#economics#economic history
67 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi! I'd LOVE to hear what your "Anger Management" WIP is about!
Haha oh I wrote this one out ages ago and will definitely come back to someday. I've got about 2.5k in outline all mapped out so once things clear up I think it'll flow well, I hope! It's a very loose adaptation of the movie Anger Management:
- Bilbo is a meditation instructor and Thorin has court-mandated anger management therapy.
- Set in Modern Middle Earth set in the Blue Mountains: Internet, smart phones, Khazad-dûm is a financial center like NYC
- Bilbo works for Gandalf in his meditation school/center "Grey Haven Meditation Center" (Dis asks "Shouldn't it be Gray Havens?" "No, we get that a lot."...The port city is "Gray Havens", Gandalf Greyhame thought it would be clever 😅)
- Gandalf and Belladonna met on a pilgrimage in (Middle Earth equivalent of Nepal...Harad?) 30-40 years ago
- Bilbo is a licensed social worker (requires a Bachelor's degree and a Master's of Social Work) which is what makes his meditation program eligible as therapy
- Appearance: wears sweater vests over a white tee and comfortable slacks with leather sandals, wears a different pair of glasses every time, horn-rimmed heavy frames, round wire-rimmed, tortoise shell half frames, dark red cats eye, orange narrow squared frames, curly hair is long enough to flop over his forehead but kept neat at the back - Thorin owned an investment firm in Khazad-dûm, wealthy and high-stakes, something where being angry and aggressive is desirable…stressful. Azog was a direct competitor involved in Shady Business. There was some kind of scandal or incident in KD that caused Thorin to become disgraced. He's moved to the Ered Luin to help Dis with the boys and get a fresh start.
- Appearance: long hair kept tied back in a tail, full beard trimmed, diamond stud earring in his left ear, wears expensive suits when working and in court but ugh no polos…hmm soft long sleeved sweaters and slacks, turtleneck with blazer, expensive shoes, maybe a short sleeve button up shirt with a geometric pattern embroidered in panels down the front, with jeans and vintage loafers (yay) a hat? Ooo classy! 😍 https://images.app.goo.gl/zeGR1Yw2nDFSs5aN6 https://images.app.goo.gl/Z5Nim4m9pgyhtAkr8 - The Blue Mountains are where Vili's family is and Dis didn't want to leave, so Thorin came to help with the boys and take a less active role in his firm, part time, virtual...maybe Dain is still there running the main business.
- Dis is a lawyer in a firm with Gloin. She struggled with nannies and sitters for two years after Vili passed in a car accident. It helps that Thorin's best friend from boarding school moved out here when he got married (Dwalin/Ori)
- Thorin complains that Azog has a hand in nearly every transaction in the Khazad-dûm stock markets, practically taken over, forced the Durins out. They come from Old Ereborian money.
What would Thorin have done to get in court? - Set up by Azog? Battery, filmed - Followed Thorin to EL from KD after whatever scandal/history and harassed him, made deals fall through, threatened his family, set up confrontation - Pale as a fish belly with a predatory smile, hulking brute wrapped in a $3000 suit, shows up in court with a little toady of a lawyer and a needlessly large bandage on the opposite side of his face from where he was struck. - Presents security camera footage with no audio that clearly shows Thorin stomping up to him, shouting and ranting, enraged look, almost unhinged, turning over a table, throwing a chair, then attacking him, throwing several punches before being pulled away by Dwalin. Thorin shifts uncomfortably under Dis' sharp gaze as the footage ends. - Initially had more severe charges but Dis represented him and got them reduced to therapy. Dis argued that he's new to town and has no history of violence here or in Khazad-dûm, that he's here to support his widowed sister and nephews. - Justice Elrond Peredhil presiding "Mr Durin, based on the evidence of security camera footage submitted in case 723 on the charges of assault and battery I find you guilty. I am ordering you to pay a fine of $3,500. In lieu of jail time, in the hopes that you may yet provide a positive role model for your young nephews, this court orders you to attend 12 hours of anger management therapy with an accredited therapist to be completed within the next 120 days." With a ringing strike of his gavel the judge intoned, "Dismissed." - Dwalin says maybe it's a good thing, Thorin gets snappy and defensive, "You're kinda provin' the point here."
Cue a bunch of cute meditation class scenes with a rag-tag bunch, Oin who falls asleep every class, Bofur whose meditation pillow is pink faux fur, etc 😁, a few dates where Thorin gets pressed and would normally have lost his head but realises he reflexively uses a breathing technique and Bilbo is so proud, and an ultimate scandal where Azog tries to get Bilbo's license revoked and Thorin's therapy invalidated due to their relationship.
#bilbo baggins#thorin oakenshield#the hobbit#bagginshield#thorin x bilbo#thilbo#the hobbit fanfiction#fanfic#tolkien#bagginshield book club#wip game#modern au#anger management
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
My post about the mess that is trad pub editorial is going around again, and a lot of people are asking "so should I go indie or go trad?" and the answer is *it depends on what you're looking for*.
[I'm referring to "indie" here meaning self-pub and "trad" meaning a publisher, though most small publishers will lean closer to self-pub in terms of distribution and whatnot]
This has always been the answer, but the reasons behind it have changed a lot. People used to say "go indie if you want full control, go trad if you want someone else to handle everything else for you". This is only partially true. Even if you go trad, unless you are part of a handful of heavily supported titles, you will be doing *a lot* yourself. From editorial (I know people who were advised to hire freelance editors or sensitivity readers on their own because the publisher wouldn't do enough) to cover art (I know people who had to walk their publisher through getting them a decent cover) to cover copy (*I* had to rewrite the jacket copy for both of my books because the first attempt was inaccurate) to marketing, odds are, even in trad, you will be doing A LOT of the work yourself, but with more barriers because you don't *own* the print rights and can't stop the publisher from doing things you highly disagree with.
So what's the benefit of trad? DISTRIBUTION. If you are trying to put out the best possible book, I stand by the fact that indie authors have the ability to make *a way better product* than trad can because they can set their own timelines, make sure things are accurate to the book because things aren't being subdivided into so many overworked departments that haven't even read it, and cater to what works best rather than what seems the most profitable. The only limit for an indie author is the time and money they're able to invest into it, but once those things are present [and you can decide how much of each are needed for your book], they have significantly more potential than the average Big 5.
But indies lack *distribution*. There is still a lot of stigma against indie books that prevent readers from picking them up or lead to readers deprioritizing them when reading or writing harsher reviews. Many libraries, bookstores, etc. can't or won't stock indie books, and a lot of professional events bar indie authors from attending. This means that even if an indie book is flawless, they will inherently be gatekept out of places like Barnes & Noble, won't be present on cataloguing websites the industry relies on like edelweiss, etc. etc. This doesn't mean that indie books have *no* distribution, but there are massive financial barriers to entry when doing it alone, and even when you are doing the same marketing/promotion/networking/etc., that work goes significantly further when booksellers/librarians/etc. will go out and stock your book vs. when most will have to turn you down for one reason or another.
So to make this simpler, I think going indie is better for *the book*. It gives you the ability to put more time and effort into it, to ensure it meets your vision, to sink your love into it without having to boil out its uniqueness in favor of mass market profits. It also gives you the room to make sure the quality is up to your standards from editorial to formatting to cover design to quality of the print run. You don't have to cross your fingers and hope your publisher doesn't fuck it all up with AI or by working your team to death. You also get more knowledge about what is happening with your book (big pubs often withhold important information or straight up lie), which means you can coordinate more effective marketing campaigns than you would if say, your publisher decided they no longer cared to market your book (which happens for most books). Finally, publishing likes to do a two-month book lifespan, meaning most books stop getting any sort of in-house support two-months after release or earlier. If you want your book to stand a chance of finding an audience slow and steady (as in, the organic way books spread), you won't get that with trad pub.
However, trad pub is better for *the audience*. If you're writing for kids or teens especially, it will be VERY difficult to reach them going indie because indie thrives mostly on ebook sales and eretailers, which minors have less access to. Getting an indie book into schools and libraries is hard if not borderline impossible, and that is how most books reach kids and teens. On top of that, you likely won't reach most indie bookstores, most libraries, and won't be allowed at many conventions and events (even if you pitch yourself), which will limit who you can reach to people who readily shop online and use social media. There are many access points in getting your book discovered that, even if you *had* a large sum of money, would be denied to you by virtue of being indie. This makes discovery harder (even beyond marketing) and means that even people who *actively want your book* may not be able to get it if it's not distributed to their country, a store they can access, their library, etc. If you're writing to reach a wide audience, something that you think is educational, or that really serves an under-served demographic, trad makes it much more likely you will actually reach those people.
Now, obviously this is just my two cents. You can choose to go trad or indie for literally any reason, even just because you like the idea of getting published by a Penguin. I don't care. People's experiences also vary, and you could be that super lucky 1% who gets doted on and everything is handled for you. This is just a big picture summation of what I tend to see for the average, midlist or quiet title. But trad is notoriously opaque and a lot of people don't realize the advances indie has made in the past 5 years and also don't realize how any of this stuff works behind the scenes, so here's some info from your local hybrid (I do both) author. And if you found this helpful, consider checking out my next book, which is now funding on Kickstarter until Oct 12th.
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
The new tariffs imposed by the U.S. on China, Mexico, and Canada will have widespread effects on American goods and services. Here’s how they are likely to impact different aspects of the economy:
1. Higher Costs for Businesses and Consumers
Many American businesses rely on imported materials, components, and products from these countries. Tariffs increase the cost of these imports, forcing companies to either absorb the costs (reducing profits) or pass them on to consumers.
Industries such as automotive, electronics, manufacturing, and retail will see price hikes, making everyday goods more expensive for American consumers.
2. Inflationary Pressure
Tariffs function like a tax on imported goods, leading to higher prices across the board.
If companies pass increased costs to consumers, inflation could rise, making goods and services more expensive and potentially prompting the Federal Reserve to reconsider interest rate policies.
3. Supply Chain Disruptions & Business Uncertainty
Companies that rely on raw materials, electronics, and auto parts from these countries may face delays and shortages, forcing them to find alternative suppliers or move production, which takes time and money.
Some businesses might restructure their supply chains by sourcing materials from other countries or increasing domestic production, but this transition isn't immediate and could further increase costs.
4. Retaliation from Trading Partners
Canada, Mexico, and China have signaled that they may impose their own tariffs on U.S. exports, which could hurt American industries that depend on international trade, such as agriculture, aerospace, and manufacturing.
Farmers, in particular, could face declining demand for crops like soybeans, corn, and dairy products, which were previously targeted in retaliatory tariffs during the Trump-era trade war.
5. Impact on the Stock Market & Business Investment
Investors dislike uncertainty. If businesses anticipate lower profits due to higher costs or potential trade disruptions, stock markets may react negatively.
Companies may delay hiring or expansion plans due to concerns over higher operational costs and shifting trade dynamics.
6. Possible Job Losses in Affected Industries
If businesses face significantly higher costs and declining demand due to retaliatory tariffs, some industries could see layoffs or reduced hiring.
Manufacturing and export-dependent sectors, such as automotive, steel, and agriculture, may be hit the hardest.
Potential Silver Linings
Some industries, like domestic manufacturing and steel production, could see short-term gains if companies decide to shift production back to the U.S. instead of relying on imports.
The government may use tariff revenues to invest in domestic industries or subsidies, potentially offsetting some negative effects.
Bottom Line
The new tariffs will likely increase costs for businesses and consumers, contribute to inflation, and create uncertainty in financial markets and supply chains. While some domestic industries might benefit, the risk of retaliatory tariffs and economic slowdown poses a challenge for the broader U.S. economy.
13 notes
·
View notes